Learn what you need to know before getting a haircut
Above all you should have a good state of mind to learn this thing, because hairdressing industry is not to be able to learn overnight, new era tells everybody to learn the thing that must know before clipping hair now, everything starts from the foundation!
01 bone characteristics
Shape is often affected by the undulation of the bones. Although the head is spherical, it is not completely spherical.
If you look at it carefully, you should be able to see that it's composed of surfaces with different angles.
The bone is divided into two curved surfaces, vertical and horizontal, so as to observe its characteristics.
02 crosscutting partitions
The top (blue) part, surprisingly much flatter than the rest, has very few vertical points going up, and most of the time it goes up diagonally at a near-vertical Angle.
Above the horn (pink) is the roundest part, the most dominant direction is obliquely upward. When the head is cut across, it is the largest part of the circumference.
The longitudinal undulation has very complicated conditions (e.g., the transverse extension of the horn, the flat head). Below the horn (yellow) is most obliquely downward.
There is a great difference between the front and back of the ear-to-ear extension line, with a flat front and a rounded back. The neck (green) is angled downwards. Tapering down the middle after joining the line of the neck.

Two - zone and multi - zone cut hair reveal secrets
03 Sectioning lengthwise
The forward part (yellow) has few points that are completely forward. The rounded part is abundant, and the oblique part (pink} is the protruding place of the anterior skull above the tau kok.
And it has to be consistent with where the contours of the face recede, so the area before and after changes dramatically. The transverse part (cream color) protrudes obliquely due to the Angle of the upper part
The underside of the ear (green) must be consistent with the hairline just behind the ear. The rear part (blue) is completely straight and the rear part is very few,
It's mostly going backwards and almost straight back. The upper part is concave because of the flat head, the middle part is protruding because of the occipital bone, and the lower part is connected with the head and neck.
There's a tapering in the middle, and there's a lot of ups and downs. As long as you remember the bulge around you, you'll be sure to have pits that are more convenient.
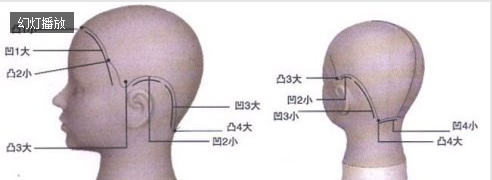
04 hairline thread
Hairline also has the same shape as bone, with very complex shape. In the cutting of contour lines, because it is often affected by the shape of contour lines,
So it's best to really remember the shape. The individual difference in hairline shape is obvious. Here are some general theories.
There are sometimes small projections near the midline of convex 1 (e.g. There is even a large sag from the midline to the sideburns (1).
It's a complicated point because there's a depression in the line of the face. Since convex 2 is the closest point on the concave 1 line to the face,
It's a little bump. So it becomes a point. Since it has the largest protrusion, there is a corner on the way to the contour line connected from the forehead to the side.
Concave 2 is the appearance of a concave line following the ear. When cutting the profile lines of the side part, the profile lines tend to be in a concave state.
This was caused by the pitch, above a pitch, above the pitch of the ears, above the pitch. Also, because it's concave behind the ear
The large concave line at the sharp Angle of the back of the head). Therefore, the overlapping area gap between the front and back of the hair will be generated. When the front area is small, it is easy to see through the situation.
Convex 4 is the projection of the sharp Angle of the posterior head. A line depicting a depression (concave 4) that is centered at this point on the midline side of the posterior neck.
Previous:Already the first article
Next:Why do all the hair salons have a barber pole in front of them?







